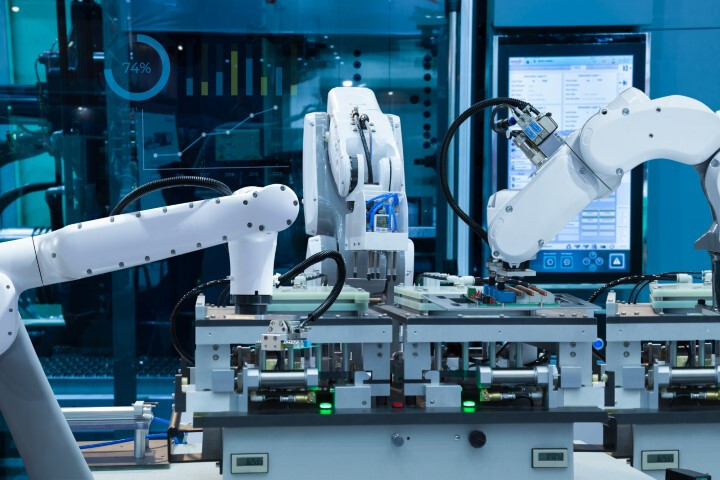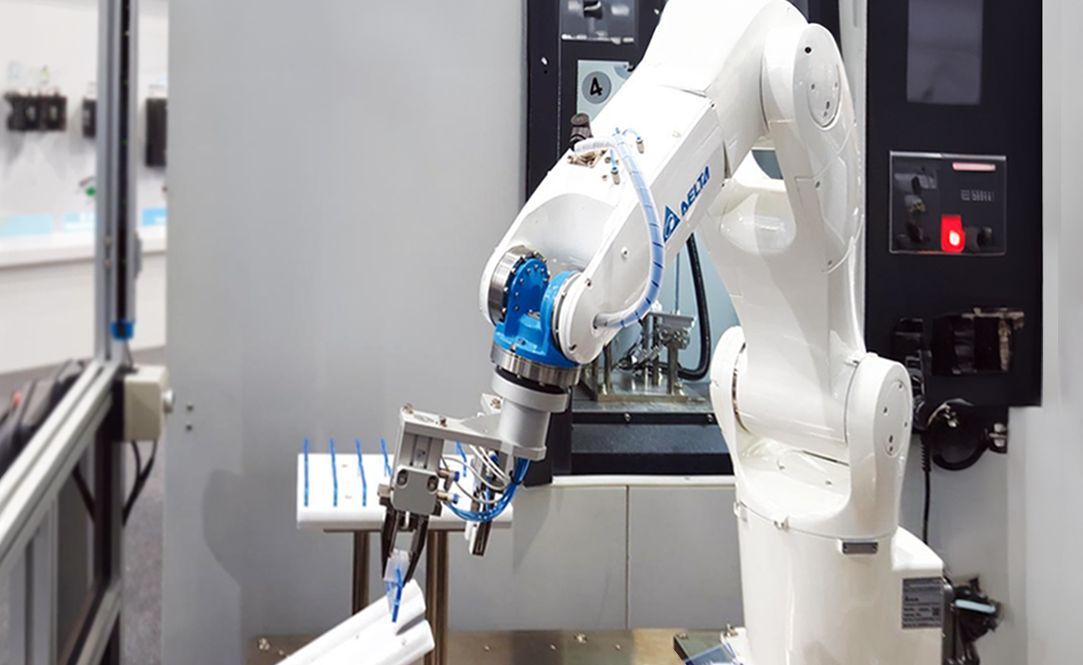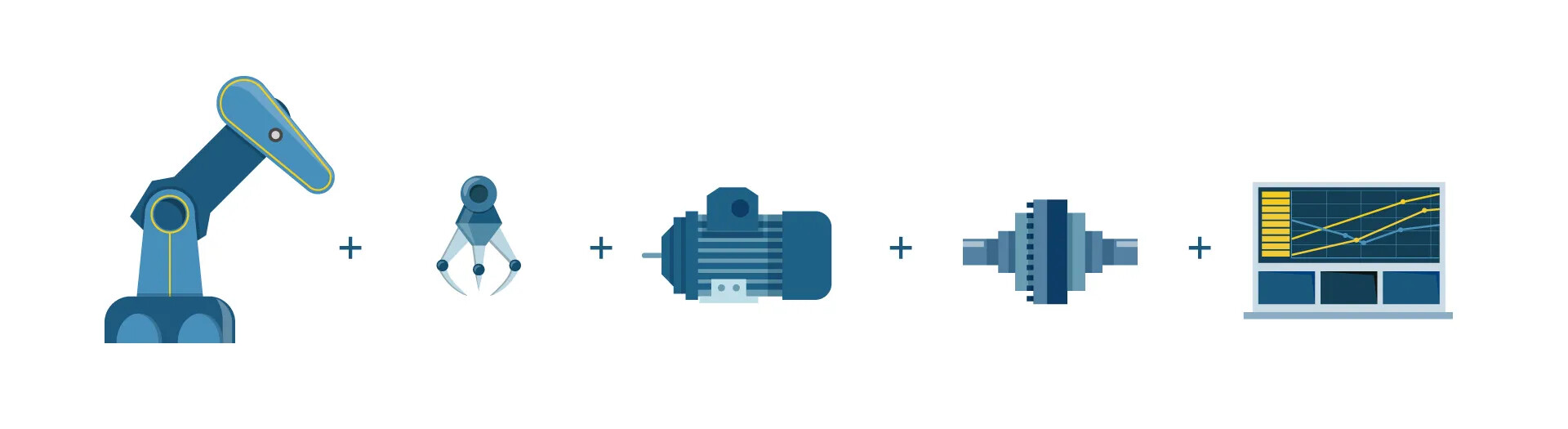

Manufacturing and assembly are two areas that make extensive use of robotic arms. To name a few, they are widely used in electronics, PCB fabrication, semiconductor-related industries, panel photovoltaics, biotechnology and medical sectors, battery manufacturing, machining, service robots, and the shoe manufacturing industry. With the rise of Industry 4.0, concepts such as unmanned factories and smart factories promise that robotic arms would replace traditional human labor completely. Ace Pillar, let us have a look today at the numerous applications, types, and uses of robotic arms, as well as the process of production line planning!
How do I use a robotic arm?
A robotic arm, is a type of automated control equipment.
Automated systems using robotic arms typically include the arm body, end effector (gripper) at the arm's tip, controller, servo motors, gearbox, sensors, and other components. A robotic arm can make repetitive and highly precise movements under programmed control, allowing it to undertake jobs that traditional mechanical devices find challenging, such as large-scale welding or precision gripping operations over broad ranges and angles.
Robotic arms, through programmed control, can execute various intricate movements, which can be translated into specified planar or 3D motions. During execution, they continuously provide feedback and make real-time adjustments to achieve extremely high precision operations.
Common driving systems for robotic arms :
Each driving approach has advantages and disadvantages. The suitable approach is determined by the application's specific requirements, which include motion range, speed, precision, payload capacity, rigidity, and cost, among other things.
Drive type | Feature |
|---|---|
Driven byelectricity |
This is the most prevalent way, in which electric motors drive the robotic arm's motion. Electric motors can be servo motors or direct current motors, depending on the desired motion precision and speed. |
HydraulicPower |
Hydraulic systems are utilized to power robotic arms, such as forklift-type handling robots, in specific applications, particularly those demanding high load capacity and high power output. |
PneumaticPower | Pneumatic drive is commonly utilized in light-duty tasks such as assembling or handling lightweight materials |
HybridDrive | Using a combination of drive methods to obtain best performance in a variety of conditions. A robotic arm, for example, may use electric drive for precision positioning while also using hydraulic drive for high load capacity operations. |
Robotic Arm with Four Axis SCARA Robot
Robotic arms are classified into four types: four-axis, six-axis, collaborative, palletizing, and so on. How do you pick the best one?
Collaborative Robot
ISO 10218-1 compliant for human-robot collaboration, removing the need for extra safety barriers. With clear teaching points and a simple flowchart programming method, production flexibility is achieved
Industrial Robot
Industrial robots, which are built for use within safety enclosures, offer greater precision and speed than collaborative robotic arms.
Ceiling Mount Robot
Ceiling-mounted fixed robotic arms save 40% more room than tabletop fixed robotic arms. This increases floor area usage and decreases blind spots in robotic arm movements.
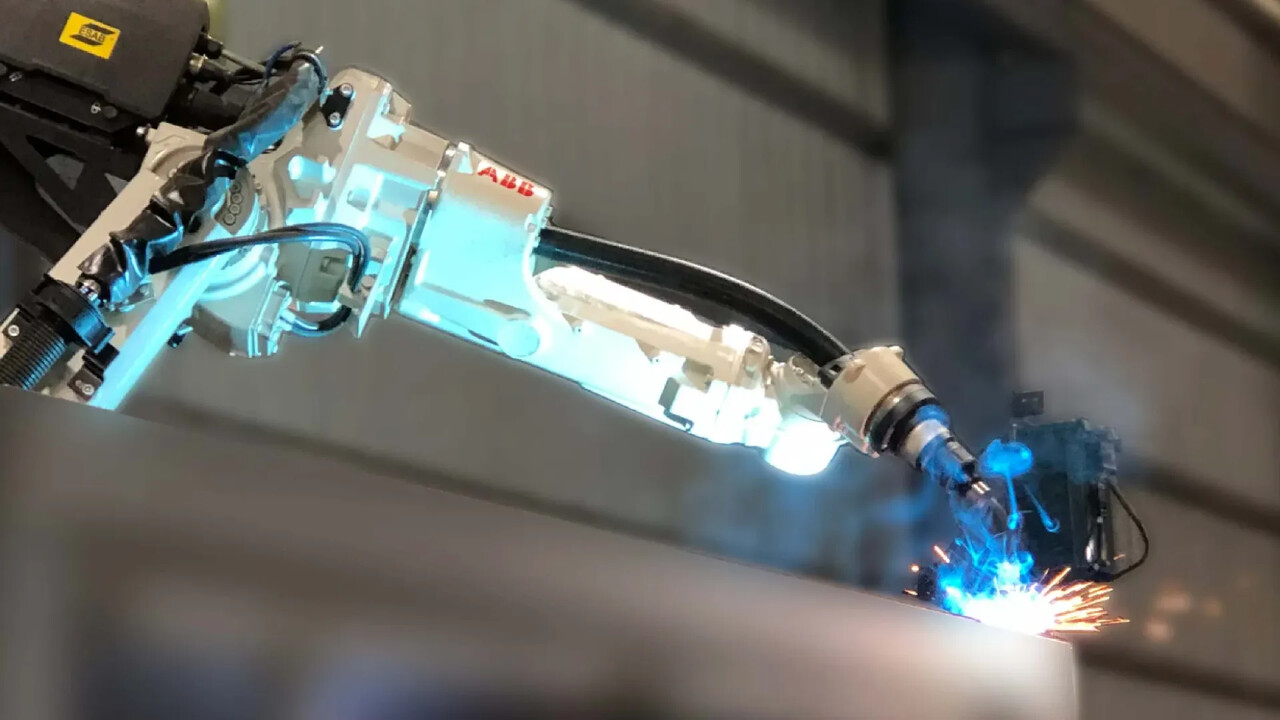
Welding Robot
Welding robotic arms reduce the need for manual labor, enhancing production efficiency, ensuring precision welding for consistent quality, and preventing personnel from being exposed to potentially hazardous working environments.
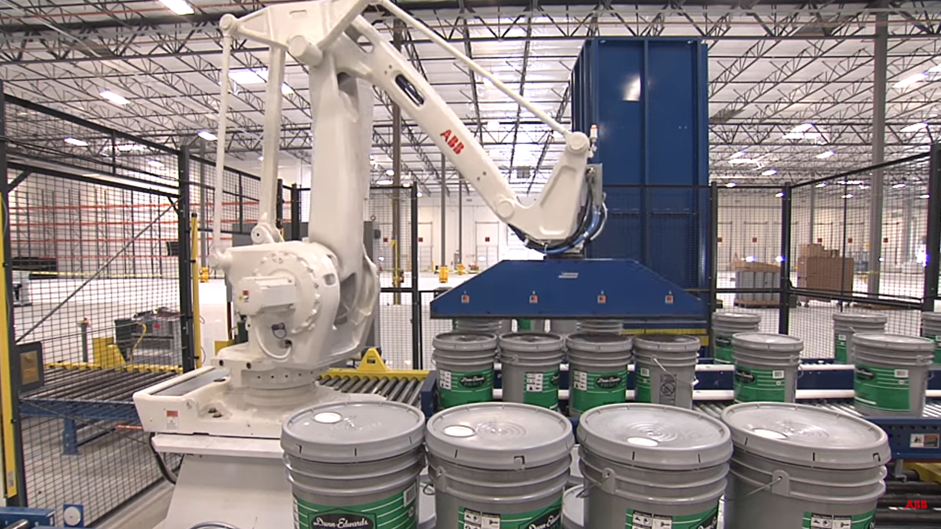
Palletizing Robot
One of the most important uses in the logistics sector. In the last step of shipping, where boxes are stacked, bagged or bottled packaging is used, efficiency is critical. Automated stacking systems improve productivity and efficiency significantly with palletizing robotic arm technologies.
What is the definition of Robotic Arm Simulation Software?
Robotic arm simulation software is a tool that permits equipment to be pre-evaluated before it enters the actual stage. It makes it easier to test product assembly procedures, production efficiency, and overall operating environment layout in advance. In Industry 4.0 factories, where robotic arms and smart sensing systems are core components, real-time communication and environmental monitoring between mechanical parts are achieved. Smart factories use big data, IoT, cloud, and high-performance computing. Furthermore, the integration of IT and OT systems, as well as the collection and analysis of robotic data, supports decision-makers in making intelligent decisions—a critical step for the manufacturing industry to attain Industry 4.0.
Complete product line and professional assessment applications.
It is critical to spend time confirming clear requirements before deciding on a certain model. Choosing the incorrect model might diminish cost-effectiveness and may result in improper use, potentially reducing the lifespan of robotic arms.
Professional consulting with Robotic Arm experts provides support in selecting the suitable model through talks and project knowledge. Parameters such as load capacity, workspace, manufacturing efficiency, inertia, and eccentricity can all be estimated using simulation software【To consult now, click the link.】